How You Can Prepare for PCI DSS Version 4
If you are conducting financial transactions with customers, your business now involves the responsibility of protecting data. Why? Because the completion of a sale means you now have sensitive financial information – credit card details, bank account numbers, personal identification data.
What happens if the data is compromised? Nothing good. Building trust between you and your customer is key to maintaining their business and your revenue. A breach of this trust can result in damage to your reputation and loss of customer loyalty, impacting the success and sustainability of your business.
What is PCI DSS?
You may be familiar with the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard often known as PCI DSS. Established by the major card brands, PCI DSS is a set of security requirements and best practices developed for organizations that handle credit card information.
The Standard serves as a crucial framework for safeguarding cardholder data and plays a crucial role in mitigating fraud and chargebacks. While specifically designed to focus on environments with payment card account data, PCI DSS can also be used to protect against threats and secure other elements in the payment ecosystem.
Compliance with the Standard contributes to fraud prevention and chargeback reduction because you can prove you have taken protective measures when it comes to your customer’s financial data.
Preparing for PCI DSS Version 4
In March of 2022, the PCI council released version 4 of PCI DSS, introducing several changes meant to strengthen payment card account data security. There has been a grace period for implementation, but as of March 31 of this year, phase one of the new standards must be in place, with phase two due March 2025.
Most organizations are prepared for the upcoming changes and have been working to make the necessary updates. You should still familiarize yourself with Version 4.0 and understand the changes from the prior version.
Of the 13 new requirements, there are seven that will impact most merchants. The key requirements include:
- Encrypting all sensitive authentication data regardless of whether the primary account number is present. This requirement ensures heightened security in handling authentication data.
- Having an automated phishing protection mechanism. This measure fortifies defenses against social engineering threats, reducing the potential for malware and ransomware attacks.
- Maintaining an inventory of all scripts on your e-commerce payment pages. This includes ensuring the integrity of each script to prevent unauthorized modifications and verifying their authorization and execution.
- 12-character passwords for users and administrators accessing cardholder data are now the norm, and you should encourage the use of passphrases for added security.
- Employing authentication methods when conducting internal vulnerability scans. This enhances the accuracy and detail of vulnerability assessments, providing a comprehensive view of potential security risks.
- Having a change and tamper detection mechanism in place to ensure unauthorized modifications are quickly reported to security personnel to maintain security.
- Finally, merchants with cardholder data environments must periodically verify their PCI scope. This involves identifying data flows, documenting storage methods, encryption, and access controls, as well as assessing any changes that may impact security.
Many of the items explained apply not just to you, but, to your vendors and partners as well. Any third-party service provider who deals with your customer’s card data must comply with the standard. If they do not, you are considered non-compliant and risk fines and a shutdown of your payment system.
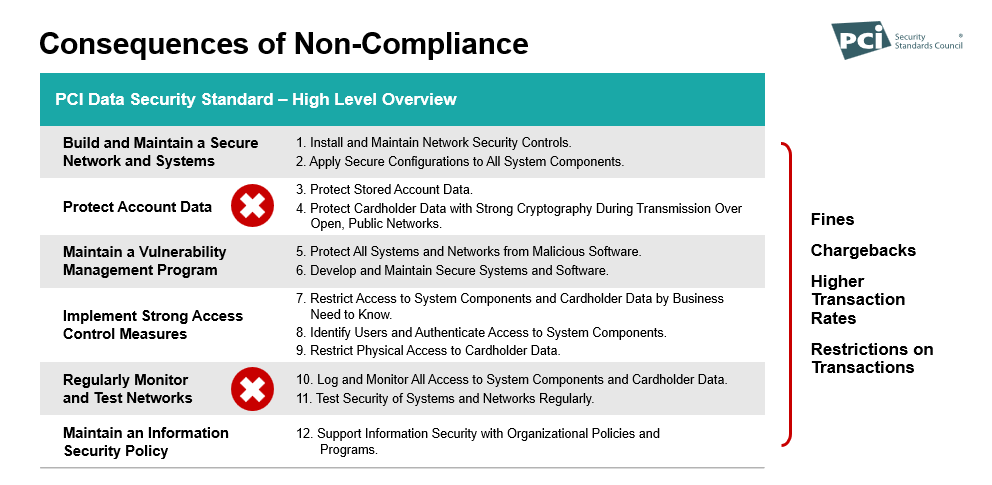
Consequences of PCI-DSS Non-Compliance
Failing to meet PCI DSS compliance can be expensive. You risk significant fines, chargebacks, higher transaction fees, and restrictions on conducting payment transactions. There are ways to ensure you are compliant. Stay up to date on PCI standards. Don’t ignore the emails from your merchant provider asking you to fill out a questionnaire (you’ll also save yourself a monthly non-compliance fee). Make sure your payment provider uses tokens.
In conclusion, maintaining compliance with PCI DSS Version 4 is vital for businesses handling credit card information. As the deadline for compliance approaches, it’s essential for organizations to prioritize the necessary updates and collaborate closely with vendors and partners to maintain a secure environment for cardholder data. By staying informed, proactive, and diligent in their efforts to meet PCI DSS standards, businesses can navigate the complexities of data security with confidence, safeguarding both their customers and their bottom line.



